When replacing a motherboard or a network card, during a P2V or cold migration of virtual machines between hypervisors, or when configuring multiple VLANs on a single NIC in Windows, you can come across a problem of hidden (ghost) network adapters. In this case, you cannot set the previously assigned static IP address for a new network adapter with the error The IP address you have entered for this network adapter is already assigned to another adapter.
Windows automatically hides the devices that are present in Windows configuration but are not physically connected to the computer. A hidden network adapter in Windows remains if you physically disconnect the previously installed network card (this can be either a physical NIC or a virtual network adapter). The previously installed network card becomes hidden and you cannot see it in the Device Manager.
The IP Address is Already Assigned to Another Network Adapter
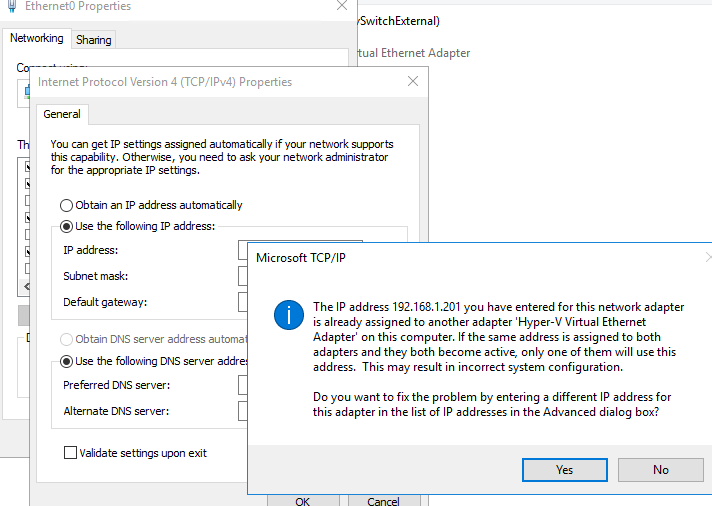
The main problem with hidden network adapters is that you cannot assign an IP address of your old network adapter to a new network interface. When you try to assign the old IP address, the following error appears:
Microsoft TCP/IP The IP address <IP address> you have entered for this network adapter is already assigned to another adapter (Intel Gigabit Network Connection) which is no longer present on the computer. If the same address is assigned to both adapters and they both become active, only one of them will use this address. This may result in incorrect system configuration. Do you want to fix the problem by entering a different IP address for this adapter in the list of IP addresses in the Advanced dialog box?
If you try to set the network adapter’s IP address using PowerShell, an error will appear:
New-NetIPAddress –IPAddress 192.168.10.155 -DefaultGateway 192.168.10.1 -PrefixLength 24 -InterfaceIndex 22
New-NetIPAddress : The object already exists. Windows System Error 5010,New-NetIPAddress
I often come across this issue in VMware virtual machines with a VMXNet3 virtual network adapter. A new virtual NIC card is identified as a new device (unlike vNIC type E1000). If you have removed a network card (vNIC) on a VMWare virtual machine and added a new one, you won’t be able to set your old IP address assigned to the removed network interface.
Also, the problem of hidden network adapters appears after migrating a physical server to a VM (Physical-to-Virtual — P2V), for example, using the VMware Converter. After migration, disabled NICs remain in Windows and you cannot assign old IP address settings to new vNICs.
Prior to assigning an old IP address to a new network adapter, you must remove the configuration of disconnected NICs.
Show Hidden (Non-Existent) Network Adapters in Windows Device Manager
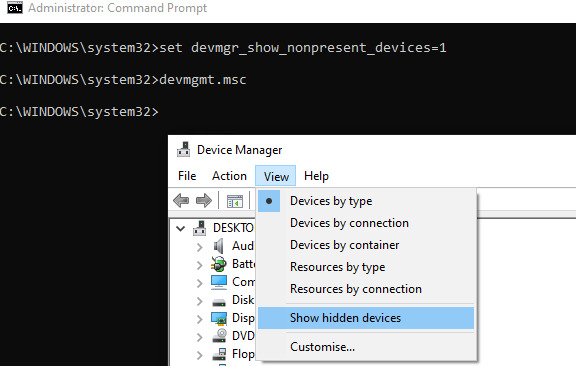
To show hidden (physically disconnected) network adapters in Windows, open the Device Manager console in a special mode. To do this on Windows 7 (and previous versions):
- Open the command prompt as an administrator;
- Run the command:
set devmgr_show_nonpresent_devices=1 - Start the Device Manager console:
devmgmt.msc
In the top menu, click View -> Show hidden devices.
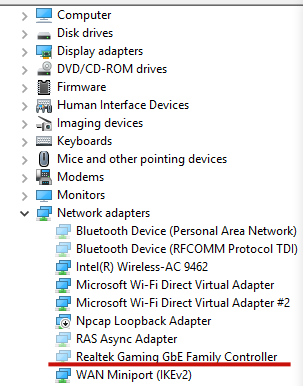
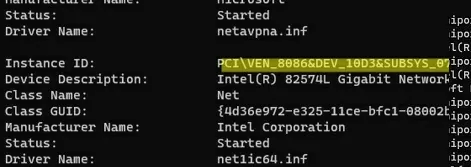
Expand the Network adapters section. Hidden network cards should appear in the list (they have pale icons). Select the network controller you want to remove, right-click it -> Uninstall Device. You can remove the network adapter driver by checking the Delete the driver software for this device option.
How to Remove Hidden/Non-Present Network Adapters with PowerShell and CMD
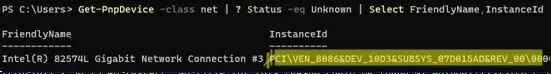
You can list unused/hidden network adapters in Windows using PowerShell:
Get-PnpDevice -class net | ? Status -eq Unknown | Select FriendlyName,InstanceId
Then you can remove such a network adapter by its InstanceId (copy its value from the previous command result):
$InstanceId = “PCI\VEN_8086&DEV_10D3&SUBSYS_07D015AD&REV_00\000C29FFFF66A80700”
$RemoveKey = "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum\$InstanceId"
Get-Item $RemoveKey | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Property | %{ Remove-ItemProperty -Path $RemoveKey -Name $_ -Verbose}
You can remove all hidden (non-present) network adapters using a PowerShell script:
$Devs = Get-PnpDevice -class net | ? Status -eq Unknown | Select FriendlyName,InstanceId
ForEach ($Dev in $Devs) {
$RemoveKey = "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum\$($Dev.InstanceId)"
Get-Item $RemoveKey | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Property | %{ Remove-ItemProperty -Path $RemoveKey -Name $_ -Verbose }}
You can use the DevCon.exe (Device Console) tool to remove devices in Windows. This tool is part of the Windows Driver Kit (WDK).
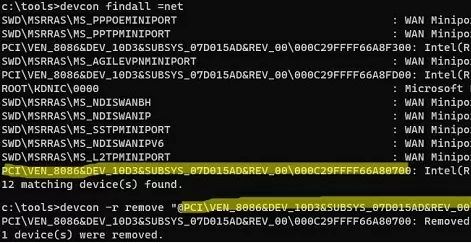
List all network adapters:
devcon findall =net
Copy the Device Instance ID of the network adapter you want to remove and run the command:
devcon -r remove '@PCI\VEN_8086&DEV_10D3&SUBSYS_07D015AD&REV_00\000C29FFFF66A80700'
On Windows 10/11 and Windows Server 2022/2019/2016, you can use the PnPUtil built-in command instead of the devcon.exe.
List network adapters:
pnputil /enum-devices /class net
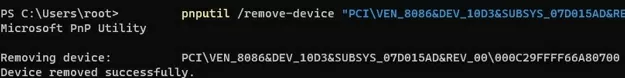
To remove a device by its InstanceID:
pnputil /remove-device "PCI\VEN_8086&DEV_10D3&SUBSYS_07D015AD&REV_00\000C29FFFF66A80700"
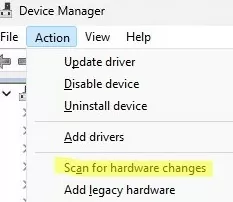
Open the Device Manager, select Actions -> Scan for hardware changes from the menu and check that the hidden network adapter has been removed.
Remove Network Adapter Settings from the Registry
If after removing the ghost NIC in the Device Manager you still cannot assign the old IP address to a new adapter, remove the IP configuration of the old NIC from the registry.
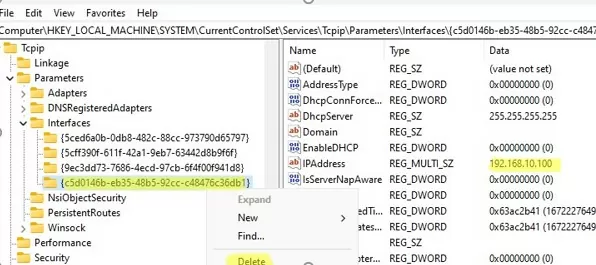
The IP settings of your network interfaces are located under the registry key HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\Interfaces.
This registry key contains some {Interface GUID} keys. Check them one by one until you find the interface, which IPAddress value contains the IP address assigned to the old network interface.
Remember the name of the registry key (it is the identifier of the network adapter). Remove the keys:
- HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\Adapters\{your_NIC_ID}
- HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\{your_NIC_ID}
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Network{your_NIC_ID}
Restart your computer and try to assign the old static IP address to a new network adapter.
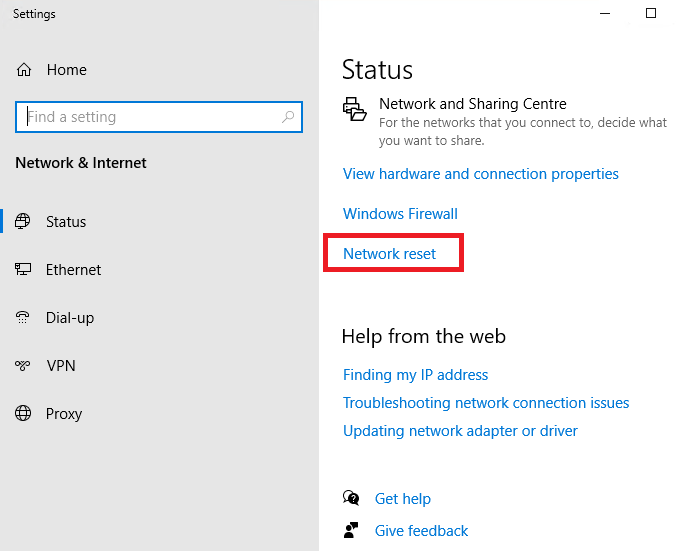
It is also recommended to reset the network settings. In Windows 10 and 11, you can do it in Settings -> Network and Internet -> Network Reset.
If you face a problem after you installed an additional network card on your computer, make sure that the built-in LAN interface is disabled in BIOS/UEFI settings (the item is usually called Onboard Gbit NIC or Onboard LAN).
2 comments
God bless you
netsh trace diagnose scenario=NetworkReset
In Windows 10, this command worked well.
It’s like clicked a network reset in the settings.